[ad_1]
William_Potter
The non-public consumption expenditures worth index (“PCE”) rose in January, year-over-year, at a 5.4 % annual fee.
Core PCE rose by 4.7 %, an increase over the December quantity. Core PCE excludes meals and power costs.
PCE Value Index (Wall Road Journal)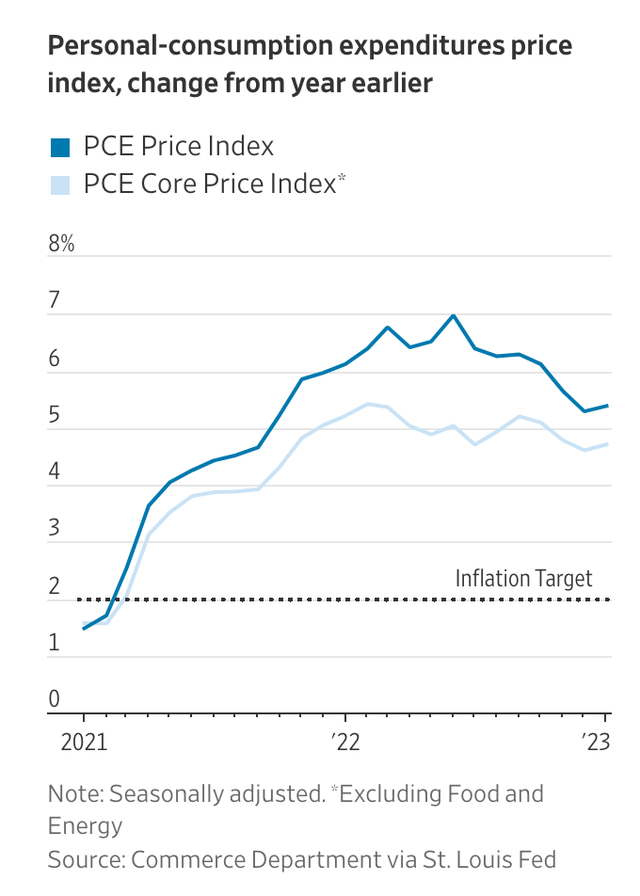
As may be anticipated, inventory costs dropped.
The S&P 500 Inventory Index was down 60 factors by 10:00 am.
Implication: Federal Reserve nonetheless has a methods to go in its battle to cut back inflation and, therefore, the Fed will probably be elevating its coverage fee of curiosity for a while into the long run and can proceed to cut back the scale of its securities portfolio.
This isn’t excellent news for the inventory market.
Quantitative Tightening
The Federal Reserve lowered its securities portfolio by solely just a little bit on this previous banking week.
Securities held outright declined by solely $3.6 billion, bringing the entire discount within the securities for the reason that “tightening” program started in the midst of March 2022 to $503.6 billion.
Nevertheless, reverse repurchase agreements rose by $108.9 billion up to now banking week, drawing down financial institution reserves by a bigger quantity.
Total, reserve balances with Federal Reserve Banks, a proxy for extra reserves, dropped by slightly below $124.0 billion.
Apparently, on the present degree of the Fed’s coverage fee of curiosity, 4.58 %, reserves needed to go away the banking system to be able to keep the speed at this degree.
The implication is that there’s loads of liquidity within the banking system and the efficient Federal Funds fee would have fallen from its 4.58 % degree if the extent of reverse repurchase agreements had not risen by the quantity cited above.
In actual fact, since March 16, 2022, the extent of reverse repurchase agreements has risen by $607 billion giving us some perception into how the Federal Reserve is managing the “tightening” program.
Sure, the Federal Reserve has lowered its securities portfolio by over $500 billion, however, serving to to easy the rise happening within the efficient Federal Funds fee, the Fed has needed to oversee one other lower in reserves as reverse repurchase agreements have risen by $607 billion.
It ought to be famous that the Federal Authorities has returned slightly below $270 billion to the banking system in deposits, a motion that elevated industrial financial institution reserves.
Since March 16, 2022, extra reserves within the industrial banking system, measured by the quantity of Reserve Balances with Federal Reserve Banks have fallen by nearly $910 billion.
Implications
One conclusion I draw from these numbers is that there’s a large amount of cash obtainable to traders within the American monetary system.
The Federal Reserve is decreasing the scale of its steadiness sheet, however it’s also counting on the “repo” market to take much more reserves out of the industrial banking system to be able to keep the Federal Funds fee on the degree the Fed designates it to be.
The extent of “reverse repos” on the Fed’s steadiness sheet is market-driven, however reveals how liquid the monetary markets are that such a lot of “repos” are wanted.
The quantitative tightening (QT) continues. The Federal Reserve needs to keep up its self-discipline on this a part of its present coverage program. Notice the “regular” decline within the Fed’s securities held outright
Securities Held Outright (Federal Reserve)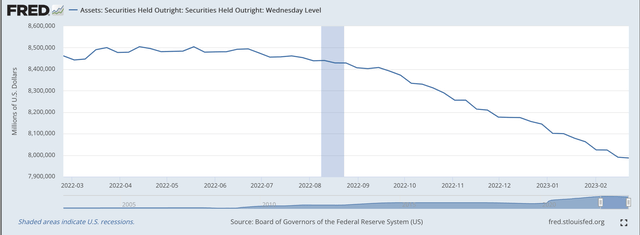
Taking a look at this chart we are able to say that the Federal Reserve actually needs to keep up a really disciplined strategy to the precise discount in its securities portfolio.
Clearly, the Fed is utilizing the “repo” market to handle the quantity of liquidity within the banking system and, within the present state of affairs, oversee the discount in financial institution reserve balances which are wanted to assist the extent of the Fed’s coverage fee of curiosity.
Drawback
The Fed, itself, has, for the reason that starting of 2020, injected tons and many cash into the banking system to avert a significant monetary disaster related with the unfold of the Covid-19 pandemic.
That’s, the Fed, itself, created an asset bubble throughout this time interval, one thing that I’ve written fairly a bit about.
Now, as we all know, the Fed is engaged in QT to be able to reverse a few of the issues that this asset bubble created.
There’s one other drawback that analysts at the moment are apprehensive about…the asset bubbles which are being created by different central banks all over the world.
Gillian Tett factors to this drawback in her column within the Monetary Occasions this morning.
Ms. Tett writes concerning the liquidity that different central banks all over the world are offering.
The Financial institution of Japan, the Folks’s Financial institution of China, and the European Central Banks have been pumping numerous cash that’s going into world markets.
Ms. Tett writes, “The online result’s that these three central banks have collectively pushed nearly $1.0 trillion of extra liquidity into the worldwide system since October (when adjusted for trade charges).”
“This greater than offsets what the Fed has achieved. Name it, for those who like, some unintentional anti-QT.”
No marvel, she states, that the U.S. inventory market has been on the rise for the reason that center of October.
S&P 500 Inventory Index (Federal Reserve)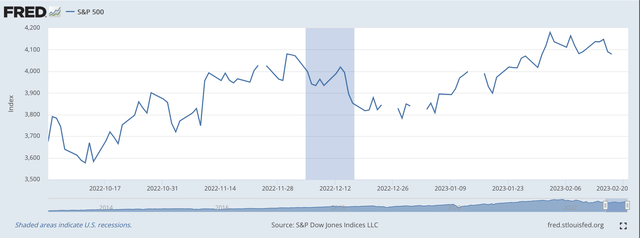
Notice that the S&P 500 inventory index (SP500) was at 3,584 on October 14, 2022 and closed yesterday at 4,014.
Wow!!! A 12.0 % rise!
Ms. Tett closes her article with this suggestion:
“The important thing level for American traders is that this: at the same time as they observe inflation knowledge, company earnings and Fed speeches at residence, they should watch what [is going on elsewhere in the world].”
So, what does all this extra liquidity on the earth imply to the Federal Reserve?
Extra work forward.
[ad_2]
Source link